
We strongly encourage users to use Package manager for sharing their code on Libstock website, because it boosts your efficiency and leaves the end user with no room for error. [more info]

Rating:
Author: janni
Last Updated: 2019-10-31
Package Version: 1.1.2.0
Category: Other Codes
Downloaded: 1745 times
Followed by: 3 users
License: MIT license
Replacement libs may supplant official mE libraries to decrease final code size and RAM use, increase speed of code execution and fix various quirks. Most of replacement libraries also add new functionality. Replacement libs cover the most substantial areas of coding and thus improve performance of other libraries that use the replaced ones.
Do you want to subscribe in order to receive notifications regarding "Replacement libraries for PIC18 & P16enh processors (mP and mB PRO)" changes.
Do you want to unsubscribe in order to stop receiving notifications regarding "Replacement libraries for PIC18 & P16enh processors (mP and mB PRO)" changes.
Do you want to report abuse regarding "Replacement libraries for PIC18 & P16enh processors (mP and mB PRO)".
| DOWNLOAD LINK | RELATED COMPILER | CONTAINS |
|---|---|---|
| 1572538324_replacement_libr_mikropascal_pic_mikropascal_pic.rar [2.97MB] | mikroPascal PRO for PIC |
|
| 1572538495_replacement_libr_mikrobasic_pic.rar [2.97MB] | mikroBasic PRO for PIC |
|
Replacement libraries form a group of libraries that may supplant official mE libraries to decrease final code size and RAM use, increase speed of code execution and fix various quirks. Most of replacement libraries also add new functionality. There are two kinds of libraries - the system libs, that are invisible to the user, like System and basic math libraries, and libraries that may be found in Library Manager, like Conversions, String, or math functions libraries. Replacement libs cover the most substantial areas of coding and improve performance of other libraries that use the replaced ones. For those that do not (yet) have a licence it may be good news that replacement libraries may allow to pack noticeably more code into the 2k words demo limit.
A Windows program, called LibsSwitch, makes installation of the replacements painless and furthermore allows to switch easily between mE libs and their replacements when desired. For easy access, one may add the program to Tools in compiler IDE by placing its name and location (compiler installation directory\Packages\RepLibs\LibsSwitch.exe) in appropriate fields in Tools\Options\Tools.
The replacement libraries, though written for mP, perform equally well in mB PRO and documentation for the latter is supplied. Note that the same archive is uploded for mP and mB and LibsSwitch may install and service libraries for one or both compilers.
Present version of replacement libraries package (1.05) was prepared for version 6.50 of both compilers. I'll try to keep the libraries updated here, though Libstock is quirky and sometimes it make take a while. Up to date version is always available at my site (link at the bottom).
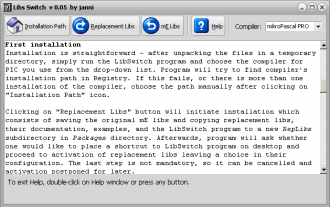
A Windows program, called LibsSwitch, makes installation of the replacements painless and furthermore allows to switch easily between mE libs and their replacements when desired.
View full imageAvailable replacement libraries:
Delays library replacement offers slight advantage in code size and decidedly more precise VDelay_ms and VDelay_Advanced_ms procedures, which are less dependent on chosen processor clock.
As the source is provided and all but one routine have same prototypes as the original, there was no need to prepare a separate documentation for this library. The additional routine, VDelay_us, allows to obtain variable delays in sub-millisecond range. It's been written in assembly, but it still has some limitations. Real 1us resolution and accuracy may be achieved only with clock frequencies in excess of 16MHz. You'll find additional information in the source file.
Strings library, prepared some time ago with yo2lio's help for PIC18 processors, has been later ported to mP PRO and expanded quite a bit by adding several Delphi-like routines. The replacement routines are more effective, both in size and in execution time, than the originals - that was the main reason to write them.
For those that use Florin's Ethernet libs a small library was added that should be used instead of his Additional Strings Library (which cannot be used in parallel with the Conversions lib replacement). It contains just few routines that differ in naming from the Strings lib replacement and are needed by Ethernet libs. It's naturally called the same as original: pic_additional_string_library.mcl as the Ethernet libs search for it.
Due to use of assembly, the Conversions library produces smaller and faster (up to several times) code than the official one and is also more extensive, introducing new functions and procedures. For those that want just smaller and faster code, but do not want to bother with changing names of routines, the library contains all routines present in the official version. In the replacement lib some routines perform similar tasks - that's because new routines work differently than those from official lib (in fact, the latter call the former and only then change the result). The official lib routines are there both for compatibility with older code and for other official libs that use them.
EEPROM libraries were prepared for processors with smaller (256 bytes) and larger (>256 bytes) internal EEPROMs – just like the official libs they replace (compiler chooses the right one for given processor based on data in appropriate definition file).
Both libraries contain the same routines, only adjusted for EEPROM size. Block read/write routines have been added to allow operation on blocks of data. One may read up to 256 bytes with EEPROM_readBlk to a RAM memory locations starting at an address specified by a pointer. The amount of data that can be stored with EEPROM_writeBlk function has been intentionally limited to 32 bytes.
Besides some marginal optimisation, the main change introduced to System library concerns only indirect function calls, i.e. calls made using pointers, and setjmp/longjmp mechanism. The original library uses Top Of Stack registers in such cases – which in turn requires blocking of interrupts for several assembly instructions. If this is undesirable, indirect function calls may be performed using PCLAT rather than TOS - and without the need to block interrupts.
There are three public routines in official System library (Swap, setjmp, longjmp), which are naturally preserved. Added public routine, FSRcontext, should be called to force the compiler to add FSR registers to context saving/restoring in ISRs. This may prove necessary if one used FSR registers directly in Pascal in both main code and ISR (or calls routines that do it). Naturally, one may perform the context saving by oneself, instead.
Math library is an improved version of the fixed-point library, free of its quirks and code-optimized to give twice smaller overall size. (Most code savings were obtained on division routines for signed numbers). In some cases it's also noticeably faster. The library comes in two versions – one of them introduces math error exception mechanism.
Problems that were corrected:
Note that problems with modulo operations, besides leading to wrong results, lead also to discrepancies between compilation-time calculations and runtime ones.
Some public routines were added to the Math library. Four of them help to exploit the exception mechanism (or just use the status byte of fixed-point calculations). There are also absolute value and square root functions as well as two additional execution-time effective multiplication routines.
The library defines also constants representing integral types' range limits.
Floating-point math library replacement has also two versions - both produce smaller code than the official one and give more accurate calculation results by fixing problems that the official lib inherited from the original Microchip library, i.e.
Both versions give access to floating-point operations' status byte. One of them may generate 'exceptions', i.e. allows to write code that contains provisions for calculation errors (like overflow, underflow, or division by zero). The library requires presence of appropriate version of Math library replacement.
Floating-point functions libraries, Trigon and Trigonometry, were prepared to work with MathDouble replacement of mE's system floating-point library (__Lib_MathDouble.mcl). Please do not use them separately, i.e. with the original MathDouble lib. Moreover, the Trigon library requires presence of other replacement libs, namely the Strings and Conversions libraries.
Both f-p functions libs contain all the routines present in the originals (though differently distributed) plus a set of additional routines. The replacement libraries produce smaller code than the originals, while giving more accurate calculation results, and allow to exploit the exception mechanism from Math and MathDouble lib replacements. Detailed differences from the originals:
Due to introduction of rounding while converting to integer types( in both implicit explicit conversion), use of replacement libs may require older code correction, as with the official MathDouble library conversion was based on truncation (the fractional part of real number was simply omitted). This issue is addressed by introducing a set of useful routines to the Trigon library - one of them, Trunc, may be used whenever rounding is not wanted. (There is also Round function which does nothing more than explicit conversion but was added for completeness.)
For clarity and ease of use, strictly trigonometric functions were moved from Trigon to Trigonometry library. All functions contained in the latter are present in official libraries and as such are documented in Help.
________________________________________
As it uses both Conversions and Math Double libraries, mE's Conversions example (..\Examples\Other\Conversions), supplied with compiler, may serve as extreme, tough somewhat tentative demonstration of replacement libraries efficiency. Results of compilation and execution of this example, after switching to PIC18 processor, are presented below
ROM [bytes] execution time [ms]
mE libs 11 093 176
replacements 4 768 54